RGB vs CMYK? Both color modes can be used in graphic design, but RGB is best for digital designs for TVs and the web, while CMYK is best for printed designs. Even so, choosing a color mode is an increasingly common dilemma among those who create graphics in various apps for later printing.
Whether you are a designer or working on a design project, it is important to understand the difference between RGB and CMYK.
That way, you’ll know which is best for your design project.
But which one is better? It all depends on what your design is used for, digital or print.
In today’s article, you will learn everything you need about the differences and similarities of the most important color modes used in graphic design: RGB and CMYK.
RGB vs CMYK: What is the Difference?
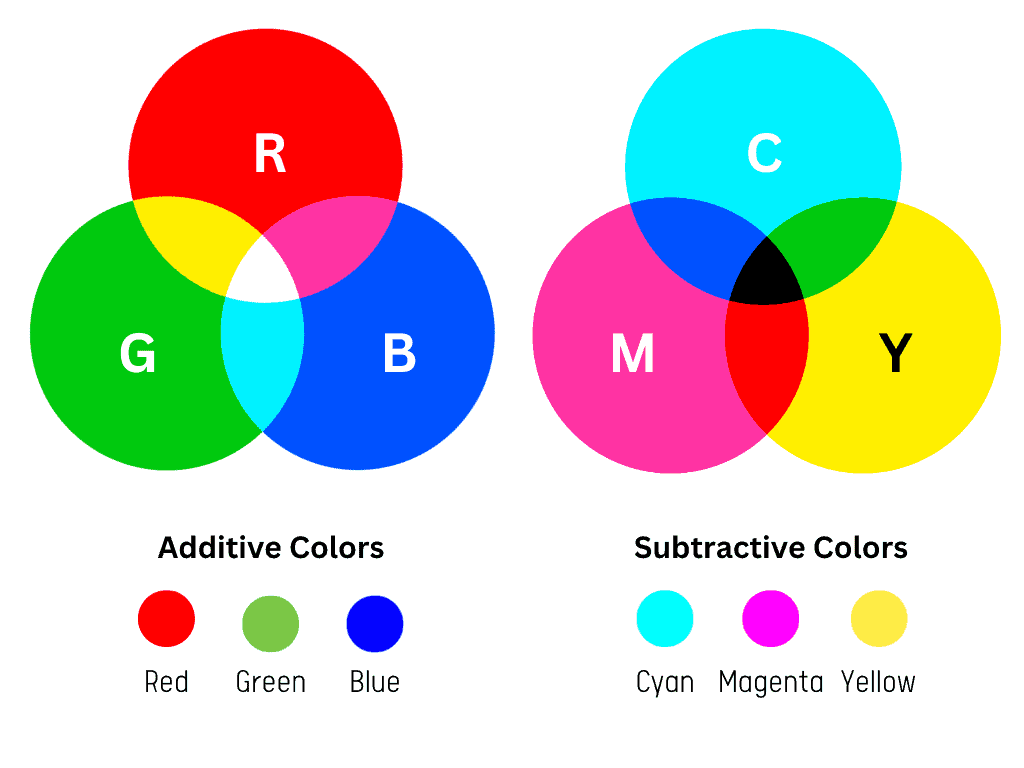
Both RGB and CMYK are color modes used in graphic design, but used in different environments.
The most significant difference between the RGB and CMYK color spaces is what the designs are used for.
CMYK is a color space used in printed designs, while RGB is a color mode used in the digital space. While CMYK uses a combination of ink pigments to produce color, RGB uses light.
It is best to use the RGB color mode when designing for digital – including web, TV, or phone designs. On the other hand, when your design is dedicated to print – flyers, cards, or T-shirts – use CMYK.
So, if you use ink, CMYK is the color mixing mode to go with. If it’s for digital screens, RGB is the best choice.
Understanding the difference between RGB and CMYK helps you optimize your design to get the desired colors.
CMY – The Primary Colors of Pigment
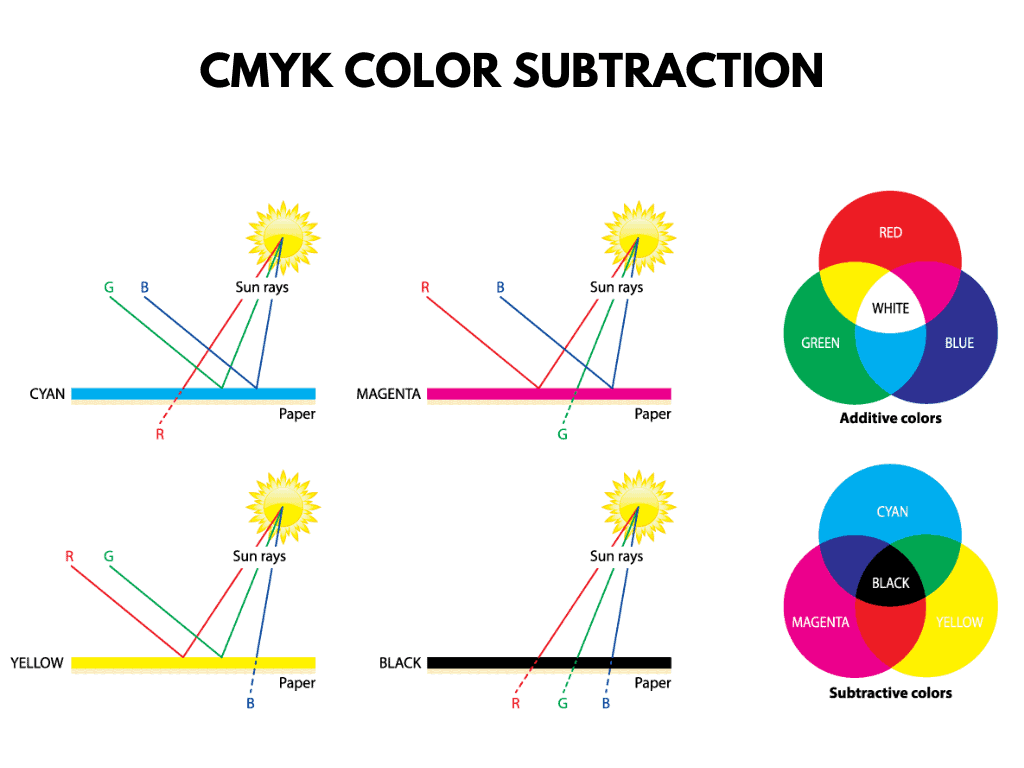
Pigments absorb light, and the process of mixing them is called subtractive mixing. The modern subtractive color model is known as CMYK.
It is called subtractive because when they are mixed, they subtract certain wavelengths of light while reflecting others.
Cyan, magenta and yellow are the primary subtractive colors because they are pure pigments that absorb (or subtract) a single frequency or color of light.
Here’s how cyan, magenta, and yellow absorb one color of light (one of additive primary colors) and reflect the other two:
- Cyan absorbs red light (or subtracts red from white light), reflecting green and blue light.
Magenta absorbs green light and reflects red and blue light. - Yellow subtracts blue light and reflects green and red light.
- Yellow subtracts blue light and reflects the green and red light.
As you can see, each pigment absorbs its complementary colors and diffusely reflects the others.
What is RGB?
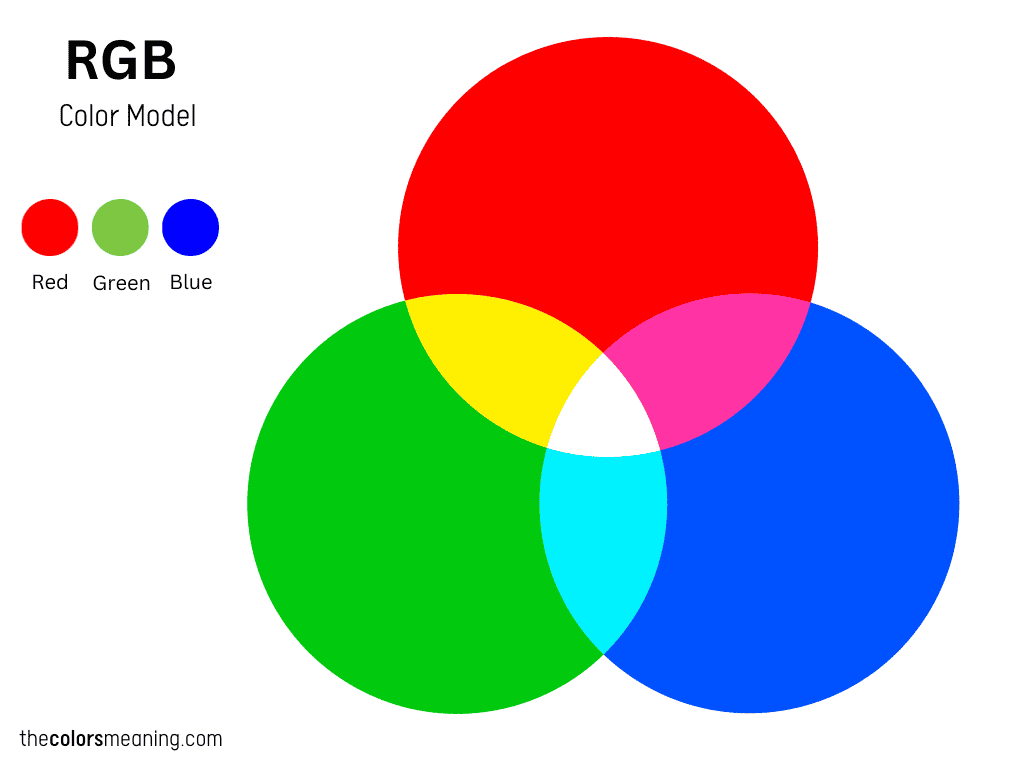
RGB is an additive color model that deals with light. Also known as Red Green Blue, this color space is for anything related to digital screens, including TVs, smartphones, laptops, computer screens, tablets, or digital cameras.
Use the RGB color space if your design will be displayed on any screen type.
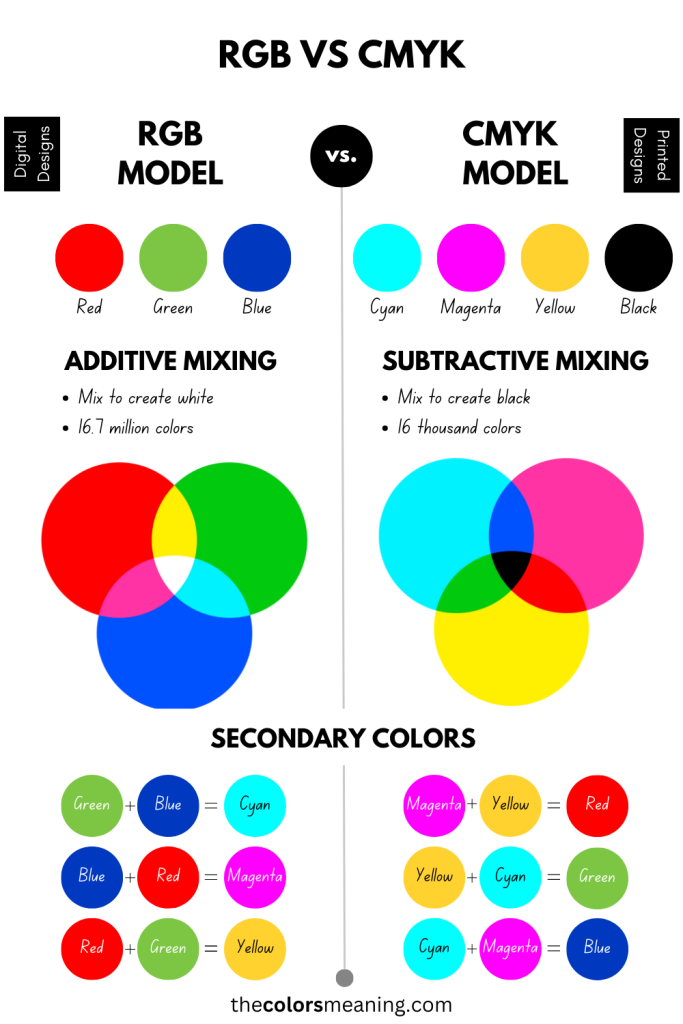
The primary colors of the RGB space are red, green, and blue, hence the acronym. When mixed in pairs of two colors, they produce cyan, magenta, and yellow – the secondary colors. These are the primary subtractive colors, meaning the primary colors of the CMYK model.
- Red + Green = Yellow
- Red + Blue = Magenta
- Green + Blue = Cyan
If you mix primary and secondary colors, you get the tertiary colors: chartreuse, spring, azure, violet, rose, and orange.
But why is RGB an additive color model?
RGB is an additive color space because it starts with black (darkness or the lack of light) and adds the primary colors of light (red, green, and blue) to reproduce the colors of the visible spectrum.
So, each primary color of light is added on top of each other to brighten the final color.
When you mix red, green, and blue at equal intensity, you get pure white.
When to use RGB?
Use RGB if your project is a digital deliverable that will be displayed on digital screens. Some examples include:
Digital Graphics:
- Websites
- Social media graphics
- Online advertisements
Digital Presentations:
- Slideshows for online presentations
- Webinars or virtual meetings
Social Media Content:
- Instagram posts and stories
- Facebook graphics
- Twitter graphics
Digital Publications:
- E-books and digital magazines
- Online brochures and catalogs
Mobile Apps:
- App interfaces and graphics
- Mobile game graphics
Video and Multimedia:
- Video content creation for online platforms
- Animations and motion graphics
Web Design Elements:
- Website banners and headers
- Navigation icons and buttons
Email Marketing Graphics:
- Graphics for email campaigns
- Newsletter designs for digital distribution
Digital Signage:
- Electronic billboards
- Screens in retail or public spaces
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR):
- Graphics and elements for VR or AR experiences
What are the best RGB file formats?
The best file formats for RGB are JPG, PSD, PNG, and GIF.
JPG
- Ideal for photographs and images with gradients.
- Used for web graphics and digital photos.
- Utilizes lossy compression.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics):
- Suitable for images with transparency.
- Used for web graphics, logos, and images requiring a transparent background.
- Supports lossless compression.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format):
- Supports animation.
- Suitable for simple graphics, logos, and images with limited colors.
- Uses lossless compression.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format):
- Suitable for high-quality images and photographs.
- Used in professional graphics software.
- Supports lossless compression.
RAW:
- Camera-specific raw image formats include Canon RAW (CR2) or Nikon RAW (NEF).
- Preserves the most data from the camera sensor.
- Requires specialized software for processing.
PSD (Adobe Photoshop Document):
- Native file format for Adobe Photoshop.
- Preserves layers, text, and other editable elements.
- Used for design projects.
WebP:
- Developed by Google, WebP is a modern image format with both lossy and lossless compression.
- Provides good compression and image quality.
- Gaining popularity for web graphics.
It is best to avoid RAW, TIFF, BMP or PDF formats as they can be space-consuming and are not compatible with common software.
What is CMYK?
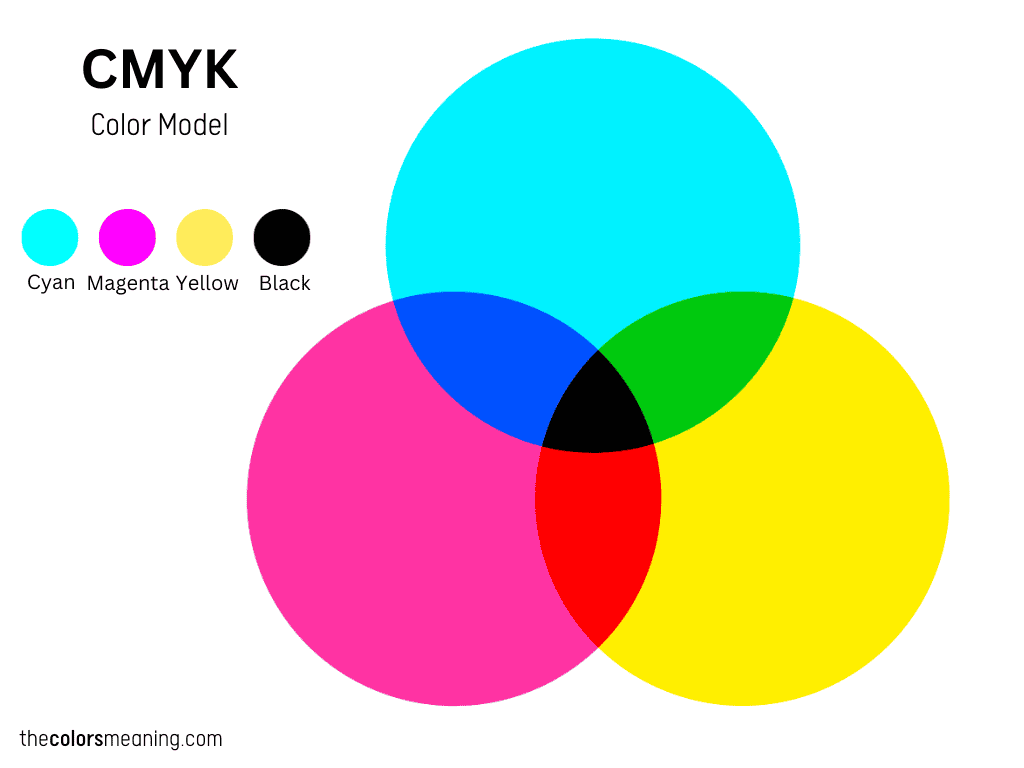
CMYK is a color space used for printed materials. It stands for cyan, magenta, yellow, and key – which is black.
Use the CMYK color space if your design is supposed to be printed.
The primary colors of this color mode are cyan, magenta, and yellow.
While cyan, magenta, and yellow are the primary subtractive colors, black is used as an additional color.
The difference between CMY and CMYK is that the latter uses an additional color to streamline the printing process and produce a pure black.
Does this mean that in CMY, you can’t produce black? In theory, mixing the three subtractive colors produces black.
In practice, you get a muddy brown because the printer inks are not so great. This is because when you combine the primaries of CMY (cyan, magenta, and yellow), they do not absorb 100% of the light. Moreover, using black is cheaper than producing it from these colors.
Even though CMY is the pillar of printing, CMYK is based on the same principle. It starts with white or a sheet of paper and gets darker and darker as you combine the colors.
Why is CMYK called subtractive? Because it subtracts the primary colors of light from white light. That’s why it’s called subtractive.
For example:
- White light – Red = Cyan
- White light – Green = Magenta
- White light – Blue = Yellow
But RGB and CMY go hand in hand because mixing two subtractive primary colors produces an additive color:
- Magenta + Yellow = Red
- Cyan + Yellow = Green
- Cyan + Magenta = Blue
So, the secondary colors of CMY are actually the colors of light.
RGB is composed of 3 channels. Each one is 8 bits, meaning that each primary color ranges from 0 to 255 (256 values). This results in a gamut of 16.7 million possible colors (256 x 256 x 256).
When to use CMYK?
When it comes to CMYK vs RGB, choose the former if your project will be printed, meaning physical material.
Go with CMYK if your project involves:
Branding:
- Business cards
- Packaging
- Signs
- Stickers
Advertising:
- Brochures
- Flyers
- Posters
- Billboards
- Catalogs
- Event Programs
- Promotional materials
- Billboards
Merchandise:
- T-shirts
- Caps
- Hats
- Mugs
- Wall art
- Branded clothing
- Notebooks
- Calendars
- Pens
Essential Materials:
- Cards
- Badges
- Certificated and awards
- Menus for restaurants
- Product labels and packaging
What are the best CMYK file formats?
The best file formats for CMYK are AI, PDF, and EPS. However, several file formats are compatible with the CMYK color model:
PDF (Portable Document Format):
- A versatile format suitable for both digital and print use.
- Compatible with most software apps.
- Can be exported with CMYK color settings for print.
AI (Adobe Illustrator):
- Native file format for Adobe Illustrator.
- Ideal for vector-based designs and illustrations.
EPS (Encapsulated PostScript):
- A vector file format used in print design.
- Supports both vector and raster elements.
- Suitable for logos, illustrations, and print layouts.
INDD (Adobe InDesign):
- Native file format for Adobe InDesign.
- Used for creating layouts for print materials such as brochures, magazines, and books.
- Supports CMYK color settings.
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics):
- Vector format suitable for print and web.
- XML-based format that can be opened with vector-editing software.
How to convert between RGB and CMYK
You can convert between RGB and CMYK for both projects and colors.
Wondering why your print colors look different to what’s on screen? That’s because RGB is an additive model that produces brightness and colors that CMYK cannot reproduce.
In short, RGB covers a range of 16,777,216 different colors, unlike CMYK, which has a much smaller color gamut.
Convert between RGB and CMYK in Apps
If you already have a project that you have started, don’t despair. You can convert between RGB and CMYK in the most popular software such as Photoshop, Illustrator or InDesign.
How to change the color space in Photoshop
In order to change the color mode in Photoshop, navigate to Edit – Convert to Profile. This will open a dialog box where you need to change the Destination Space.
Since there are several CMYK libraries, you will see more options. For general projects, choose one of the first two options. However, it is advisable to check with your printer for compatibility.
If the image is not already flattened, make sure you check Flatten Image to Preserve Appearance. This will ensure that the transparency or blending layers look the same as on screen.
How to change the color space in Illustrator
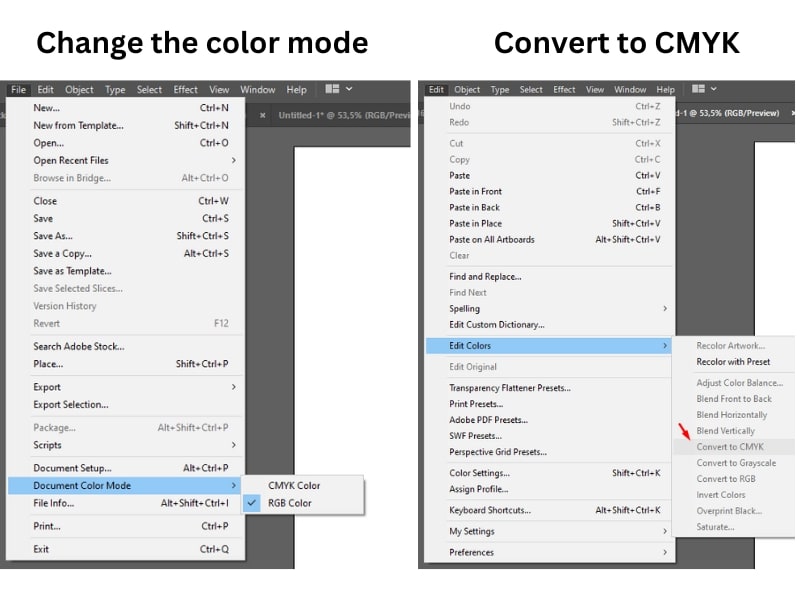
To change the color space from RGB to CMYK in Adobe Illustrator, navigate to Edit – Edit Colors and select Convert to CMYK.
If it doesn’t appear, the project is already in CMYK. This way, you can go back to RGB.
How to change the color space in InDesign
To change the color mode in InDesign, navigate to File – Adobe PDF Presets and click on [Press Quality]. In the dialog box that appears, go to the Output section and select the desired color mode for Destination.
Although it seems an extremely useful solution, it is better to change the color mode of your images in their native programs, such as Photoshop or Illustrator.
How to convert colors from RGB to CMYK and vice versa
When it comes to colors, you can convert online from RGB to CMYK and from CMYK to RGB.
Here are two calculators to help you do that:
Last Words
When it comes to graphic design, there is no one best model. That’s because each one is intended for different purposes. While RGB is best for digital work, CMYK is ideal for print products.
While RGB is better for screens and TVs, CMYK is best when it comes to printed materials.
Did you enjoy this article about the RGB vs CMYK? Share it with your friends to choose the best option.